- Aa Bb Cc
- What is compensation and benefits?
- What is compensation benchmarking?
- What are compensation data providers?
- What is a compensation framework?
- What is compensation management?
- What are compensation metrics?
- What is a compensation philosophy?
- What is a compensation review?
- Dd Ee
- What is an employee bonus?
- What are employee benefits?
- What is an employee incentive plan?
- What is equity compensation?
- What is executive compensation?
- Ff Gg
- What is the gender pay gap?
- Hh Ii Jj
- What is job architecture?
- What is a job family?
- What are job levels?
- What is job title inflation?
- Ll
- What is location-based pay?
- Mm
- What is a merit cycle?
- Oo
- What is an offer letter?
- What is on-target earnings (OTE)?
- Pp
- What is pay equity?
- What is pay progression?
- What is pay transparency?
- Rr Ss
- What are salary bands?
- What is a salary freeze?
- What is the salary midpoint?
- Tt
- What is a target percentile?
- What is total rewards?
- Uu Vv
- What is variable pay?
- Ww Xx Yy Zz
Building a compensation and benefits plan? You're in the right place.
Whether you're designing a compensation structure for the first time, looking for a clear explanation of vesting schedules to share with your wider team, or just need a quick refresher on the difference between adjusted and unadjusted gender pay gap, this article gives an overview of all the key concepts and terms you need to be aware of.
Aa Bb Cc
What is compensation and benefits?
Compensation and benefits (also known as rewards or remuneration) encompasses all forms of payment that an employee receives from an employer during their time of employment, in return for their time and work – base salary, any additional form of monetary reward e.g. equity or bonuses, and non-monetary rewards (benefits or perks) such as paid time off, healthcare, or pension contributions.
Compensation and benefits is also referred to as ‘comp and ben’ or ‘rewards’, and is also used to refer to the discipline within a company’s HR team i.e. a Compensation and Benefits Manager.
Some Reward teams think about compensation and benefits in terms of direct and indirect compensation.
What is direct compensation?
Direct compensation is any cash compensation granted to employees which holds ‘direct’ monetary value – base salary, cash bonuses, commission pay, overtime pay, etc.
What is indirect compensation?
Indirect compensation refers to any non-monetary compensation granted to employees which has ‘indirect’ monetary value, such as health insurance, pension contributions, learning and development funds, etc.
What is compensation benchmarking?
Compensation benchmarking – often referred to as salary benchmarking – is the process of evaluating your company’s compensation in comparison to the wider industry.
The core aim is to ensure that your compensation (salary, equity, variable pay, benefits) is fair and competitive for employees compared to the competitors who you compete with for talent.
Regular compensation benchmarking exercises also ensure that employee compensation remains in-line with your compensation philosophy as the talent market shifts and changes – for instance, if demand for a certain role increases in the market, then its typical salary may also increase, and the salary of your employees in that role may no longer reflect the 60th percentile you aim for in your compensation philosophy.
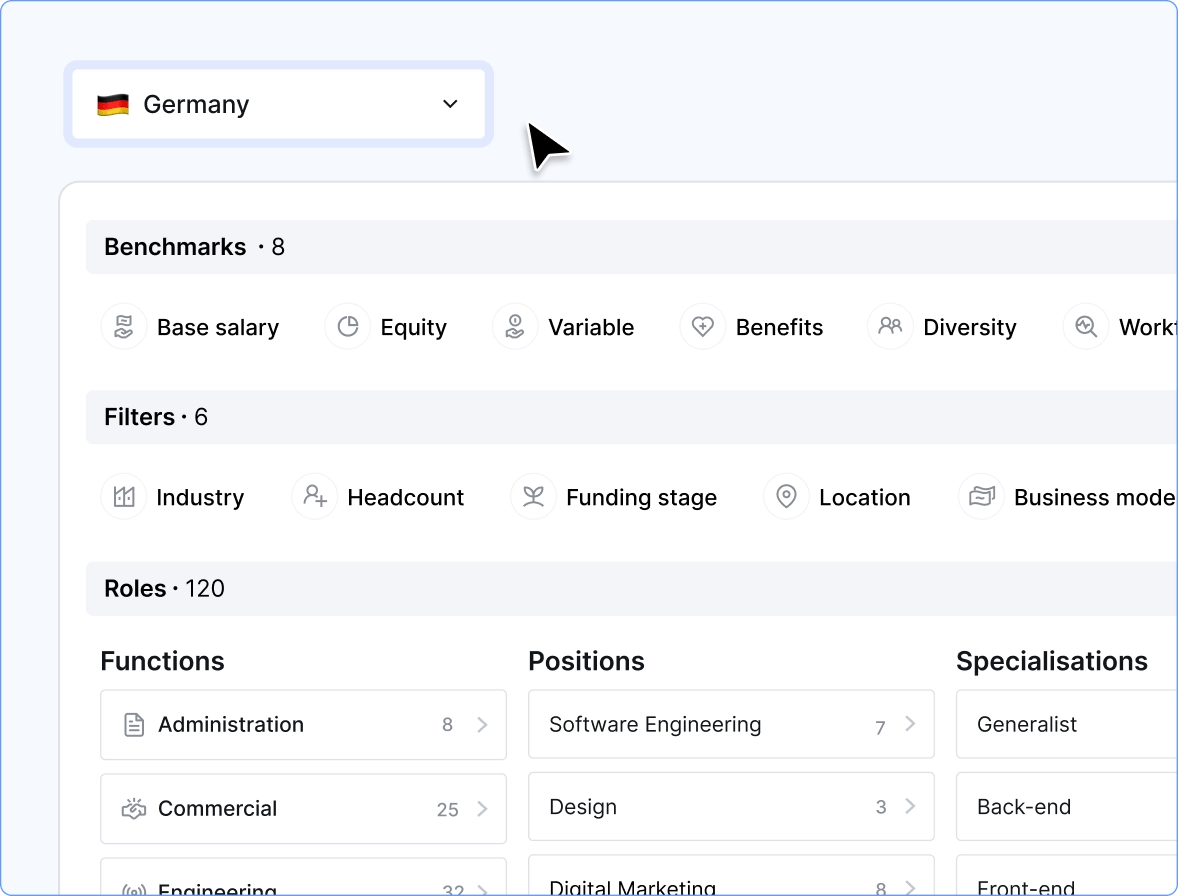
Salary benchmarking in Ravio
What are compensation data providers?
Compensation data providers provide the market data that you need to conduct a salary benchmarking exercise.
Today, providers like Ravio or Pave offer real-time compensation benchmarking data (sourced by integrating directly with company HRIS and ATS systems) within compensation software – enabling teams to benchmark compensation whilst also performing other compensation management functions such as refreshing salary bands in-line with the latest market data or conducting a compensation review.
Traditionally, companies would buy a dataset from HR consultants like Radford or Mercer who conduct wide-scale salary surveys once or twice a year.
What is a salary survey?
Salary surveys are the traditional method for delivering salary benchmarking data.
Conducted by large global HR consultancies like Mercer and Radford, salary surveys collect compensation data from large enterprises across different industries, levels, and regions. The consultancy then sells the resulting dataset back to People and HR teams, giving them the market pay data they need to understand how companies generally pay for specific roles, seniority levels, and industries.
Salary surveys have several limitations when using for salary benchmarking:
- Outdated market data due to annual or biannual surveys, and long collection cycles.
- Risk of data inaccuracy due to human error during the survey submission process
- Peer groups that don’t match your reality due to the focus on broad global enterprises
- Inconsistent job mapping that undermines benchmarking accuracy
- Challenging to use survey data, due to the sheer volume of data, the poor functionality of large spreadsheets, and the lack of support to map the external benchmarks to your internal job architecture
- Lengthy manual survey submission requirements for HR and Reward teams.
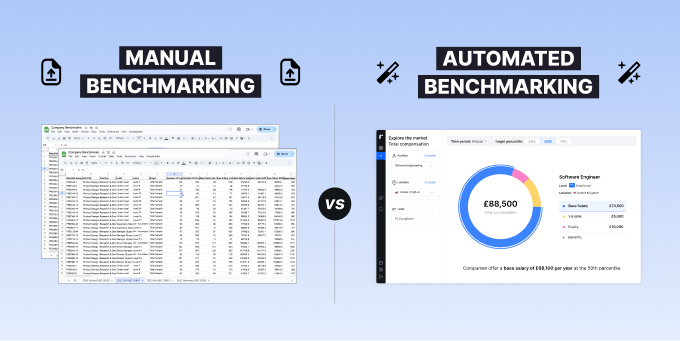
What is a compensation framework?
A compensation framework is the structure used to design and implement a company’s approach to compensation and benefits and ensure consistent compensation decisions are made across the organisation.
The compensation framework takes the principles from the compensation philosophy, and brings them to life through a set of key structures: job architecture (including job title conventions, role descriptions, job evaluation), level framework, salary bands.
What is compensation management?
Compensation management refers to the overall process of defining compensation packages for employees, administering their compensation, and adjusting it over time to keep in-line with the wider market and to reflect their performance and progression in role.
In smaller companies compensation management is typically handled by the HR or People team, whereas larger companies may introduce dedicated compensation or Rewards professionals.
Today many compensation management software providers (like Ravio) have developed platforms to streamline and automate the processes involved in compensation management – such as building and maintaining salary bands or analysing pay equity.
What are compensation metrics?
HR and Rewards teams use compensation metrics to analyse the effectiveness of their compensation strategy and to make informed decisions about changes to both individual employee compensation packages and the wider strategy.
Common compensation metrics include:
- Employee turnover rate
- Average employee tenure
- Compa ratio
- Internal pay equity
- Pay range spread
- Total cost of workforce
What is employee turnover rate?
Employee turnover rate (also known as employee churn or employee attrition rate) is a measure of the percentage of employees who leave an organisation within a specific time period – usually calculated annually.
Employee turnover rate is used as a key indicator of the health of the workplace and compensation strategy, with a high employee turnover indicating there may be issues to resolve.
Employee turnover rate is calculated by taking the number of employees who left the company in a given year and dividing this by the average number of employees the company had in that year (number of employees at the start of the year plus the number of employees at the end of the year, divided by two). The resulting figure is then multiplied by 100 to get a percentage.
Some companies also differentiate between:
- Voluntary and involuntary employee turnover or attrition – employees who chose to leave the company to work elsewhere vs those who are terminated or made redundant.
- Regrettable and non regrettable employee turnover or attrition – employees whose departure is a loss to the company vs those who will have a neutral or positive impact on leaving the team.
What is average employee tenure?
Average employee tenure refers to the typical length of time that an employee will spend with an employer. It's an important metric to monitor in relation to employee retention – the ideal is for the company to retain great employees for as long as possible, which relies on career and pay progression opportunities.
The findings from our most recent Compensation Trends report found that the average employee tenure in the European tech industry is currently 2 years.
What is compa ratio?
Compa ratio (also referred to as market ratio) assesses how an employee’s salary compares to the midpoint of the salary band for their role. If the resulting ratio is 1.0, the salary is exactly at the midpoint of the range. Anything less than 1.0 means the salary is below the salary midpoint, and above 1.0 means it is above.
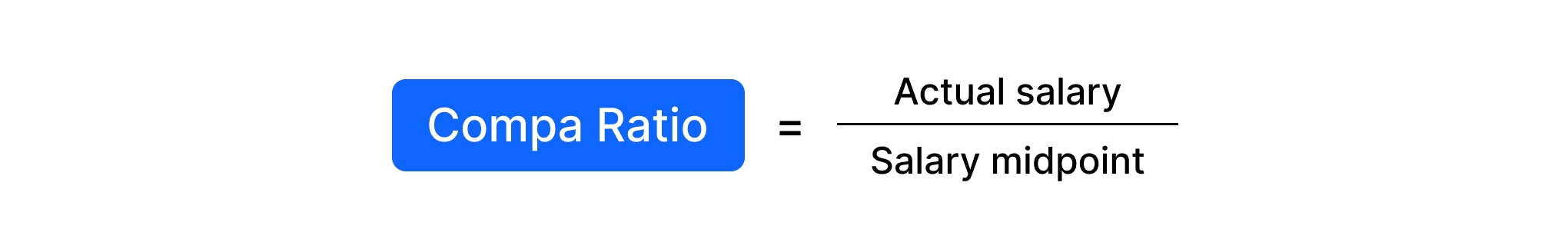
Compa ratio is used to assess whether employees are being paid fairly and competitively against market rates and their peers, as well as to measure and monitor employee pay progression through their salary band.
It’s often used during compensation reviews (mostly commonly through a merit matrix) to determine how high an employee’s salary increase should be – employees who are low in their salary band will receive a higher increase to bring them back to market alignment.
What is Total Cost of Workforce (TCOW)?
Total Cost of Workforce (TCOW) measures overall company spending on all employees – from recruitment costs to payroll costs to employer taxes to office facilities to training budgets, and much more. It’s typically used during compensation budgeting discussions.
What is a compensation philosophy?
A compensation philosophy documents a company’s approach to employee compensation, the core principles which underpin how all compensation decisions are made.
The compensation philosophy should be informed by the company’s overall values, goals, priorities, and culture.
It typically includes top-level decisions such as how market competitive a company is aiming to be with base salaries – will they be leading the market at 90th percentile pay to attract the very top talent, matching the market at 50th percentile to be in-line with talent competitors, or lagging the market at 35th percentile as an early-stage startup with limited cash?
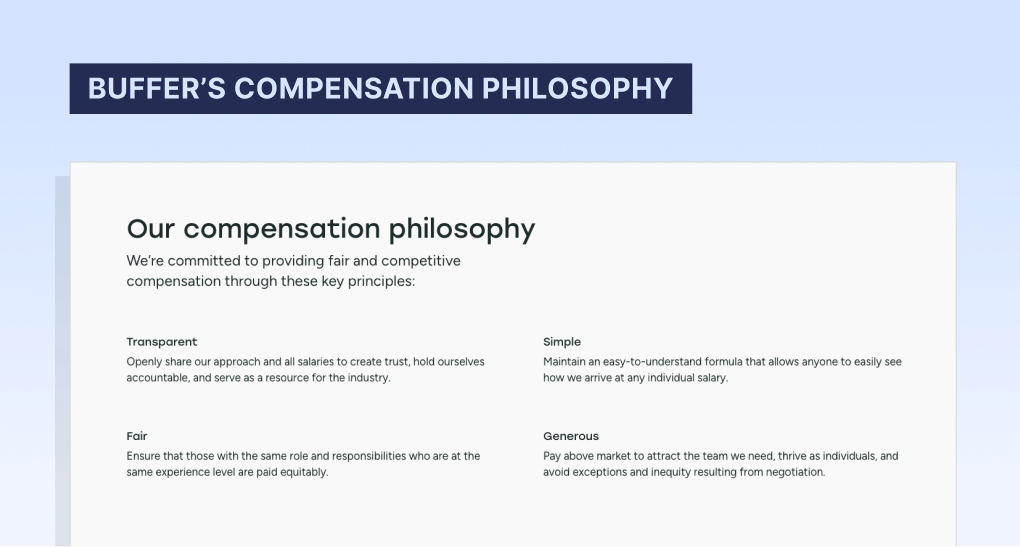
Example: Buffer's compensation philosophy
What is a compensation review?
A compensation review (also known as salary review, pay review, merit cycle) is the process of evaluating employee compensation to ensure it is fair, competitive, and aligned with the company’s compensation philosophy, and making adjustments as needed.
Most companies have a regular process of annual or bi-annual compensation reviews, with off-cycle adjustments made where there is a particularly strong case. However, there is a trend towards ‘always-on’ models of continuous feedback and compensation adjustments made as needed throughout the year – Buffer and Netflix are examples of companies who use this approach.
Many companies couple a compensation review with a performance review, with the resulting performance ratings informing compensation adjustments that are made during the compensation review – rewarding high performers with a higher salary increase, for instance. This is typically referred to as a ‘merit cycle’ because it involves salary increases made based on ‘merit’.
During a compensation review, there are many ways that a company might make changes to an employee’s compensation. These include:
- Cost of living adjustment
- Market adjustment pay increase
- Inflationary pay rise
- Performance based salary increase
- Promotion increases
- Bonus
- Equity refresher
What is a market adjustment pay increase?
A market adjustment pay increase is when an employee’s salary is increased to reflect changes in the market for their role or level.
The talent market is always shifting due to the external economic environment as well as changes in demand for certain roles or skillsets, which impacts typical compensation packages for those roles.
Market adjustment pay increases ensure that employees’ salaries remain fair and competitive by checking their salary against up-to-date market data via a compensation benchmarking tool like Ravio.
What is a cost of living adjustment (COLA)?
A cost of living adjustment (COLA) is an increase made to an employee’s compensation to reflect an increase in the cost of living (rent, goods, services) in their location.
If an employee’s salary remains the same when cost of living increases, it means they will have less buying power and less disposable income because more of it must be spent on the cost of living, which is why many employers incorporate this into pay reviews.
An increase to employee compensation based on changes in the costs of goods and services, reflecting that these changes will make a big difference to the monthly outgoings of employees.
What is an inflation pay rise?
An inflation pay rise is an increase to an employee’s salary made to reflect inflation in the wider economic environment and ensure employees remain fairly paid.
For instance, if the inflation rate in the UK was 5% in a given year, a company might choose to give all employees a 5% inflation pay rise to keep their salaries at pace with inflation – and they may then add additional increases on top of this e.g. merit increases to reward high-performing employees.
What is a performance based salary increase?
A performance based salary increase (or merit increase) is an increase to an employee’s salary made to reflect their performance in their role, with the highest performing employees receiving the highest salary increase.
What is an equity refresher?
An equity refresher (or equity refresh grant) is when an employee receives an additional grant of equity e.g. stock options.
Some companies use equity refreshers as a way to reward performance during a compensation review, and employees may also receive equity refreshers to reflect changes in market-standard compensation for their role or level, or to reflect a promotion to a new level.
Dd Ee
What is an employee bonus?
An employee bonus is a monetary payment made to an employee on top of their base salary at the employer’s discretion. Some companies use bonuses to reward performance during a compensation review – either individual, team, or company performance.
What are employee benefits?
Employee benefits are non-salary components of compensation which an employer awards to an employee in exchange for their work or time.
Employers are legally required to provide some employee benefits such as pension contributions or paid time off – which vary from country to country e.g. in France the statutory minimum holiday allowance for a full-time worker is 25 days whereas in Germany it is 20 days.
Employers may choose to go above and beyond the legally required statutory minimum for these benefits to provide a more competitive employee benefits package.
Employers may also offer benefits or perks that are not legally required, such as learning and development budgets or a range of discounts.
What are personalised benefits?
Personalised benefits (sometimes called flexible benefits) allow employees to select the employee benefits package that best suit their individual needs and circumstances, from a range of benefits choices available.
It's typical for employers to have a set of core benefits which all employees receive by default (including statutory requirements per country e.g. pension contributions), with the personalised or flexible aspect layered on top.
What is an employee incentive plan?
An employee incentive plan is a variable compensation programme designed to motivate employees to meet certain targets or goals that are important for the company’s overall objectives.
Employees are rewarded for meeting those targets through additional compensation which goes above and beyond their normal compensation package – typically a bonus or commission structure, or additional equity compensation.
There are many different types of employee incentive plan in compensation, with a few of the most common being:
- Short-term incentive plan
- Long-term incentive plan
- Sales incentive plan
What is a short-term incentive plan?
A short-term incentive plan (STIP) is a type of employee incentive plan where employees are rewarded for achieving short-term business goals – typically based on performance within a period of one year (or even less).
It’s most common for short-term incentive plans to be focused on cash bonuses based on hitting targets – especially common in sales teams.
What is a long-term incentive plan?
A long-term incentive plan (LTIP) is a type of employee incentive plan where employees are rewarded for progress towards long-term company goals and strategic objectives.
It’s most common for long-term incentive plans to be focused on equity compensation, due to their long-term focus and mechanisms like vesting schedules that mean the reward is paid out over a longer period of time.
What is a sales incentive plan?
A sales incentive plan is a type of employee incentive plan where sales team members are rewarded for achieving specific sales targets or milestones, motivating the team towards hitting those goals and contributing to the company’s revenue targets.
It’s very common for compensation packages for sales team members to have a base salary and a commission element based on meeting targets – often referred to as on-target earnings (OTE).
What is equity compensation?
Equity compensation (sometimes called share based compensation) refers to employees being granted an ownership stake in their company, as part of their compensation package.
Equity compensation is typically used as a way to incentivise and motivate employees, because they have a financial stake in the success of the company – if the company’s valuation increases, the equity will increase in value over time. It’s therefore common for equity to also be used in ongoing retention, such as granting equity refresh grants to high-performing employees or based on employee tenure.
Equity can be granted to employees through a range of different vehicles, with the most common being stock options, virtual stock options (VSOPs), and restricted stock options (RSUs). Many countries have tax efficient schemes to incentivise employers to give equity to employees, such as the EMI scheme in the UK.
Equity compensation is one of the most complex areas of compensation and benefits, with many confusing terms like ‘dilution’ or ‘exercise’ or ‘strike price’. All of these (and more) are covered in our comprehensive guide to equity compensation for startups.
What is executive compensation?
Executive compensation (or executive pay) refers to the compensation packages designed for executive or C-suite team members within a company – such as a CEO or CFO.
Different companies compensate their executive team in very different ways, depending on the size, stage, and profitability of the company. Because of this, it can be difficult to find relevant compensation benchmarking data to inform executive compensation.
Ff Gg
What is the gender pay gap?
The gender pay gap is a measure of equality in pay: the difference between average earnings for men and women.
The gender pay gap is typically calculated by first finding the difference between the average (mean or median) earnings of men or women e.g. their annual salary. This is then expressed as a percentage by dividing it by the average (mean or median) male earning and multiplying it by 100.

The resulting figure is the gender pay gap for the company.
This is sometimes referred to as an unadjusted gender pay gap, because it is the raw difference without accounting for non-discriminatory factors which may impact pay differences between male and female employees, such as job level or experience. An adjusted gender pay gap accounts for this through a regression analysis.
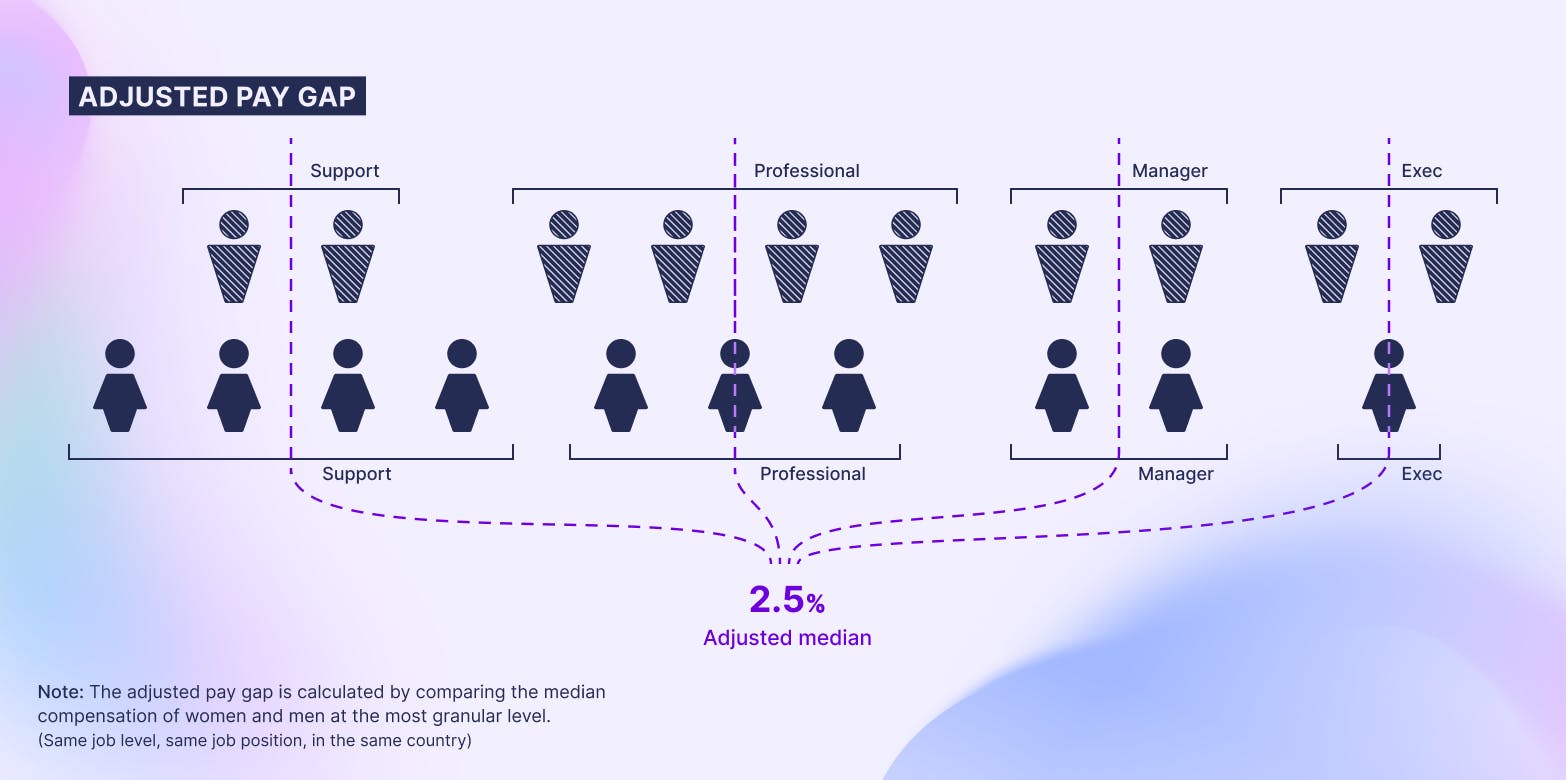
Hh Ii Jj
What is job architecture?
Job architecture is a structured framework used to bring consistency in how an organisation defines and groups all of the jobs within the company.
The job architecture defines the organisation’s job functions, job title conventions, job levels, job descriptions for each role and level, and career pathways to advance through each level.
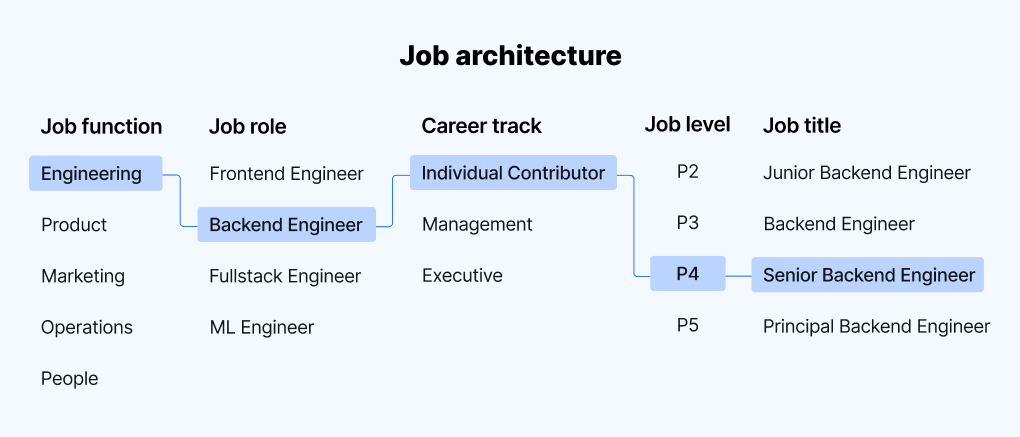
What is a job family?
A job family – otherwise known as a job function – is a group of job roles which are similar in terms of overarching knowledge and skillset e.g. Marketing, Product, Software Engineering.
Job families are a core structure in organising job roles within an organisation, and it’s typical that all roles within the same job family will operate with the same job levels, salary band structure, and career pathways to bring consistency and fairness.
What are job levels?
Job levels define the hierarchy of seniority levels within an organisation, from entry-level to manager to chief executive.
It’s typical for a company to have one set of job levels for the entire organisation to ensure consistency in how employees are able to progress their career, meaning that each role will have the same number of job levels – this overall structure is known as the job levelling framework.
Each job level should have a clear definition of expectations: the skills, responsibilities, level of autonomy, business impact that is expected at each level of seniority. This ensures clear career pathways and expectations for employees.
What is a job levelling framework?
A job levelling framework is the hierarchical structure of job levels within an organisation – defining each level of seniority that exists in that particular company.
This ensures that decisions can be applied consistently across the organisation in terms of which level of seniority an employee is hired at, and when they are ready to be promoted to the next level.
The level framework also forms the foundation for accurate compensation benchmarking, ensuring a like-for-like comparison between internal employee levels and the levels used by the compensation benchmarking data provider.
What is job title inflation?
Job title inflation refers to a senior level job title which doesn’t align accurately to an employee’s responsibilities, salary, or business impact.
In early-stage startups, for instance, it’s common for first hires in a department to receive a ‘Head of’ job title to account for lower salary offers e.g. Head of Marketing, Head of Sales – when in reality they’re performing at a mid-level.
Job title inflation can cause big issues with maintaining fair and consistent compensation because levels are inaccurate (especially as that startup’s team scales and new levels of seniority are brought in) and can lead to difficult conversations about changing job titles later down the line.
Ll
What is location-based pay?
Location-based pay is a compensation approach where employee salaries are adjusted to reflect the local market in their working location to maintain fairness in buying power and disposable income.
Different companies approach this in different ways – the best practice approach is to use global salary benchmarking data from a provider like Ravio to understand the talent market in each employee location, but many companies will use a cost of living multiplier or geographic differential for simplicity.
What is a geographic pay differential?
A geographic pay differential is an approach to location-based pay where salaries are adjusted to reflect the employee’s working location, typically grouping countries based on similarity in cost of labour – relevant for companies with hybrid or remote working models where not all employees are based in the HQ location.
Typically, a company will use their HQ location as the core location to base the geographic pay differentials on. Compensation benchmarking data is then used to assess the cost of labour in other working locations of employees compared to that HQ.
The result might be a set of tiers e.g. high cost of labour at 1.5x HQ salary, medium cost of labour at 1x HQ location, low cost of labour at 0.75x HQ location. Or it might be a differential per country – depending on how granular the company wants to be with its approach to location-based pay.
Geographic pay differentials allow companies to adjust compensation based on location, but with a slightly simpler approach than each salary being fully bespoke based on global compensation benchmarking data. This reduces administrative strain as there is less variation in how salaries are calculated (also meaning less salary bands are needed) but it does also reduce the accuracy of salaries, given the variances in each market globally.

What is a cost of living multiplier?
A cost of living multiplier in compensation is when a company adjusts employee salaries to account for the relative cost of living in their working location – relevant for companies with hybrid or remote working models where not all employees are based in the HQ location.
A data source like Numbeo’s cost of living index is used to determine how cost of living compares in each employee location, and a set of multipliers is created based on this.
For instance, Germany has a score of 58.4 on Numbeo’s cost of living index. If a company headquartered in Germany and uses the German market as their reference point for determining fair salaries, but was hiring a remote employee based in Portugal, which has a much lower cost of living at 41.2, they might account for this by multiplying the new employee’s base salary by a cost of living multiplier of 0.8. This ensures all employees performing similar roles have a similar buying power and disposable income, avoiding inequities based on working location.
However, this is not the recommended approach for location-based pay. Cost of living is just one factor, alongside others like supply vs demand for a specific role and location – which can actually have much more of an impact on market data. Therefore, relying on cost of living alone to determine salary differences per location can be unreliable. Instead, reliable global salary benchmarking data from a provider like Ravio should be used to accurately determine fair salaries per employee location.
Mm
What is a merit cycle?
A merit cycle is the process that companies use to evaluate employee performance and make compensation adjustments based on the results – combining performance reviews and pay reviews into one process as part of a ‘pay-for-performance’ approach.
What is a merit matrix?
A merit matrix is a framework for making fair decisions on salary increases during the merit cycle, based on a combination of employee performance and their existing salary band position.
This ensures that high-performers are rewarded for their contributions, whilst also ensuring that large inequities do not arise because of the merit cycle process. As an example, if two employees received the same performance rating and were in the same salary band, but one was low in the band whereas the other was towards the salary band maximum, then the one with a lower position would receive a higher salary increase.
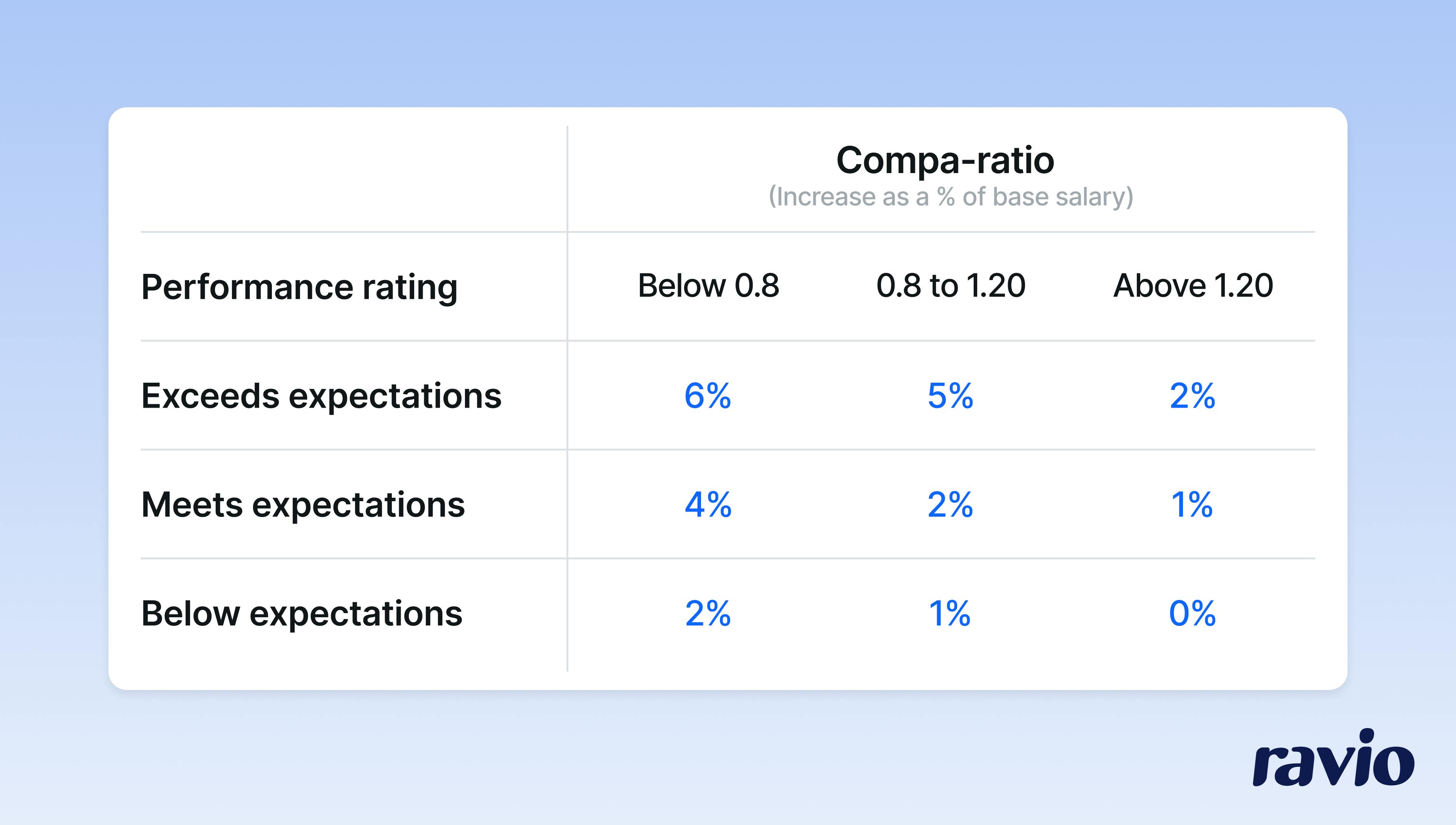
What is a merit pool?
A merit pool is the budget which is dedicated to the merit cycle and to providing salary increases to employees to keep their pay fair and competitive and to reward their performance.
What is a merit increase?
A merit increase is a salary increase rewarded to an employee ‘on merit’ i.e. to reward them for their high performance within their role.
What is pay for performance?
Pay for performance (P4P) is a compensation strategy wherein employee pay is tied to their performance in their role.
Companies who use a pay for performance model will typically run merit cycles, combining performance reviews with pay reviews to reward high-performing employees with larger compensation increases. They may also have additional levers to reward performance, such as an employee bonus programme or an equity refresh programme to reward employees who meet targets.
Oo
What is an offer letter?
An offer letter is a written document which formally offers a new role to a candidate, and typically also outlines key terms including the compensation and benefits package which is being offered to the candidate for the role. It is often the final stage in a recruitment process.
What is on-target earnings (OTE)?
On-target earnings (OTE) refers to the total monetary compensation received by an employee who has a base salary and a variable pay component, commonly used to reflect commission for sales teams.
OTE is the maximum amount this employee can earn if they are ‘on target’ for their performance and are therefore receiving their maximum variable pay on top of their guaranteed base salary.
Pp
What is pay equity?
Pay equity is the principle that equal work (or work of equal value) deserves equal pay, regardless of any differences in employee race, gender, age, national origin, sexuality etc.
Pay equity is becoming increasingly important for compensation and benefits teams, as pay transparency and pay equity legislation increases globally.
What is pay progression?
Pay progression – also known as salary progression – is the process of an employee’s salary increasing over time as their skills, experience, and impact at their role and level increases. This ensures their pay remains fair and competitive throughout their tenure in that role, as they move towards promotion to a new role or level.
Pay progression is typically measured through compa ratio or salary range penetration.

What is pay transparency?
Pay transparency is the practice of a company openly sharing salary information with existing employees and prospective job candidates, in order to increase pay equity.
When information about how salaries are determined is transparent, it means that employees and candidates are better able to identify and question any discrepancies in pay equity between themselves and peers performing equal work or work of equal value – which pushes employers to fix the underlying issues and improve pay equity.
The importance of pay transparency in driving pay equity is reflected in growing pay transparency legislation across the world, particularly notably with the EU Pay Transparency Directive.
Rr Ss
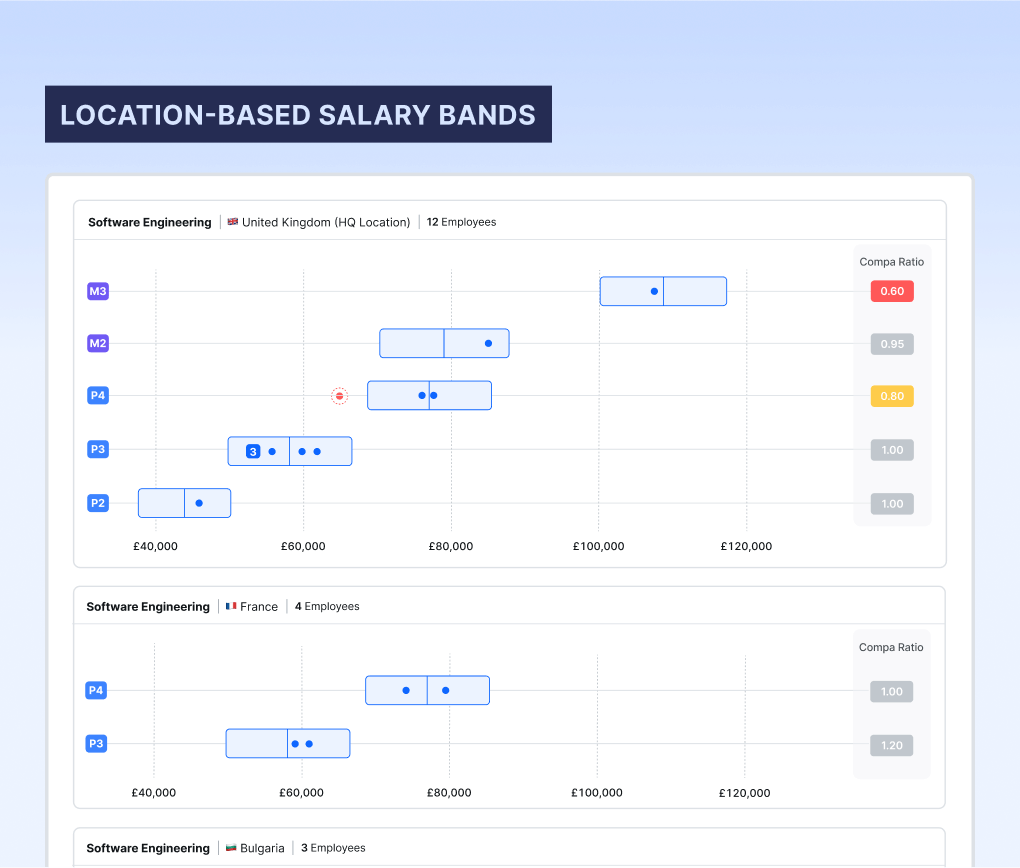
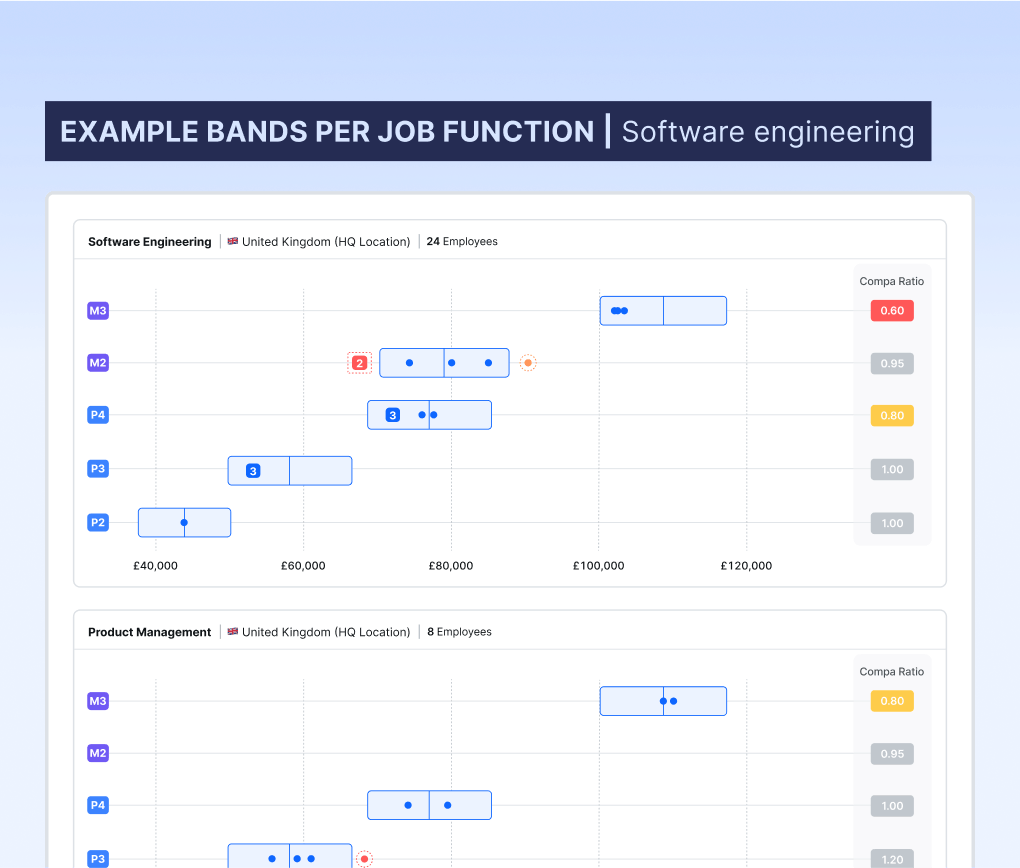
What are salary bands?
Salary bands – also known as pay bands or salary ranges – are defined salary ranges applied to a set of job positions within a company, bringing structure, consistency, and fairness to salaries for that group of roles.
Different companies approach salary bands in different ways, but the best practice approach would be to have a set of salary bands for each separate job role – and a salary band for each job level and location within that job role.
This granular approach ensures that employees with similar context (i.e. performing work of equal value and in a comparable labour market) are paid within the same range.
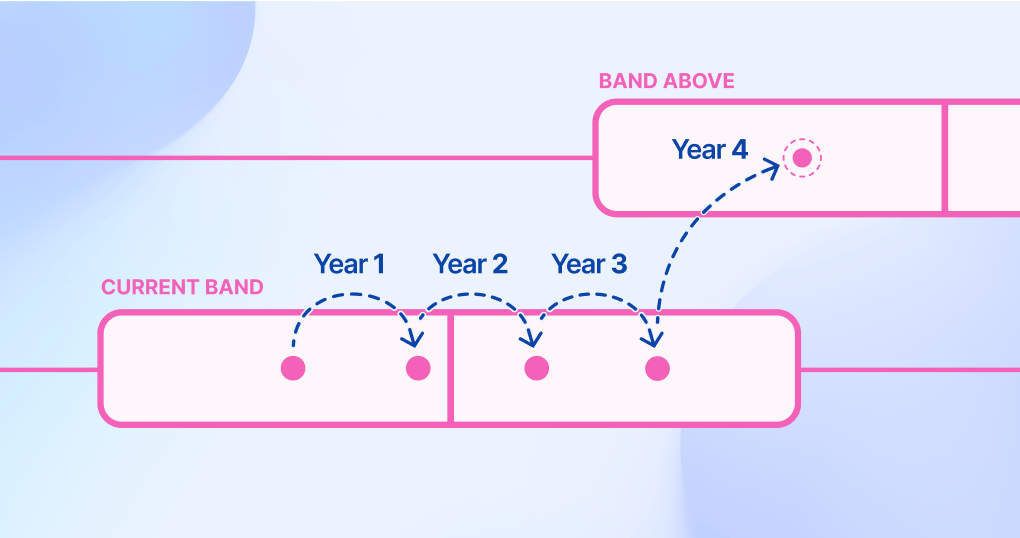
Salary bands also inform pay progression within an employee’s existing role. The band minimum reflects the lowest possible salary an employee at that role and level should receive, and the band maximum the highest possible salary.
As an employee’s skills, experience, and impact in their role increases, they should receive salary increases to reflect this, and so their band position will increase over time as they progress through the band and towards promotion to the next level (and band) up.
What is a salary freeze?
A salary freeze is when a company decides to suspend salary increases for a certain period of time. This often happens across-the-board due to financial constraints within the business.
However, it could also be a salary freeze for a specific employee e.g. to reflect that they are paid much more highly for their role and level than their peers, and so should not receive an increase to allow for pay equity.
What is the salary midpoint?
Salary midpoint refers to the middle value of a salary range, which typically reflects the market median salary for that role and level. Therefore, if an employee is paid at the salary midpoint for their salary band, their pay is on par with market rates for their role and level.
Tt
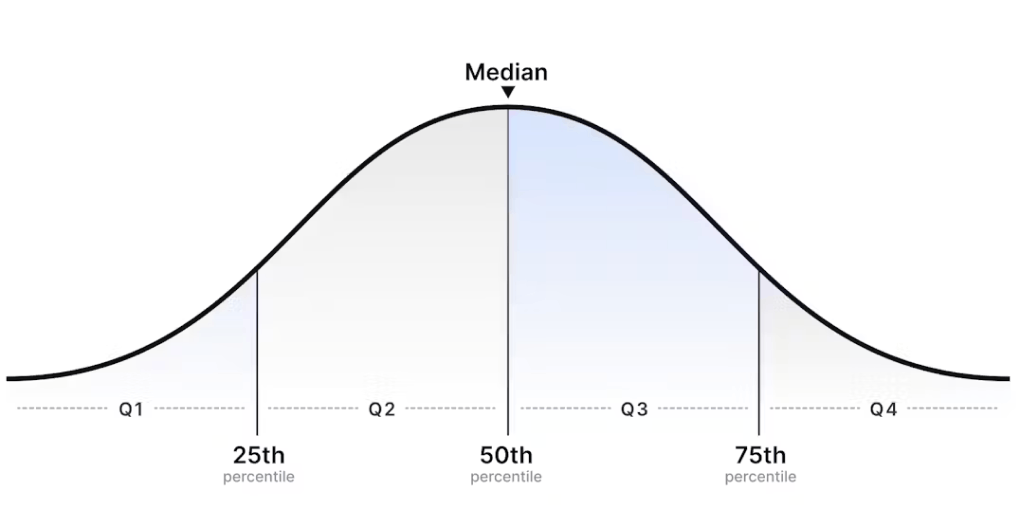
What is a target percentile?
Target percentiles in compensation are a statistical figure used to define an employee’s salary in relation to the wider market for that role – used broadly to refer to how a company positions themselves in the target market, often defined within a compensation philosophy.
The 50th percentile salary refers to the market median salary for a given job role and level – meaning that 50% of companies pay above that salary, and 50% below it. The 75th percentile means that 25% of companies pay above that salary, and 75% below it – reflecting a very competitive salary for that role and level.
What is total rewards?
Total rewards – otherwise known as total compensation or total remuneration – refers to complete package of compensation and benefits that an employee receives from their employer in exchange for their work, including base salary as well as additional components such as commission, bonuses, equity, and benefits.
What is a total reward statement?
A total reward statement is a document shared with an employee which breaks down their complete compensation and benefits package – including base salary as well as additional components such as commission, bonuses, equity, and benefits.
Employees typically receive a total reward statement when they start a new role, and then an updated total reward statement every time they receive a change in compensation e.g. a salary increase after an annual merit cycle.
Uu Vv
What is variable pay?
Variable pay – also known as variable compensation – is a form of cash payment granted to employees in exchange for their work on top of their base salary, but which is not guaranteed and is dependent on the employee achieving pre-defined targets.
It’s very common for sales teams to have a variable pay element (usually ‘on-target earnings’) to their total compensation package to incentivise team members to meet defined revenue targets.
Bonuses are another common form of variable pay, where employees are granted a cash bonus if they meet defined performance targets (either as an individual, department, or company as a whole).